Activity 2.1 | ECE Leadership: Role & Characteristics
Leadership Styles
Leadership Styles
A leadership style in an ECE manager's context refers to how you approach your tasks and interact in your role. Your leadership style directs the way in which you direct and manage staff, make decisions, and behave in your professional settings.
Kurt Lewin et al. (1939) defined three distinctive leadership styles:
- Autocratic (authoritarian) leadership
- Democratic (participative) leadership
- Laissez-faire (delegative) leadership
On the following pages, you will examine each leadership style (Lewin et al., 1939) in more detail and consider the leadership style(s) you most closely align with.
You should note that Leadership styles can change situationally and over time. You may also notice that a single individual may display a combination of leadership styles at any given moment. It is also arguable that a mixture of all leadership styles is optimal (Aronson, 2001; Günzel-Jensen, 2018)
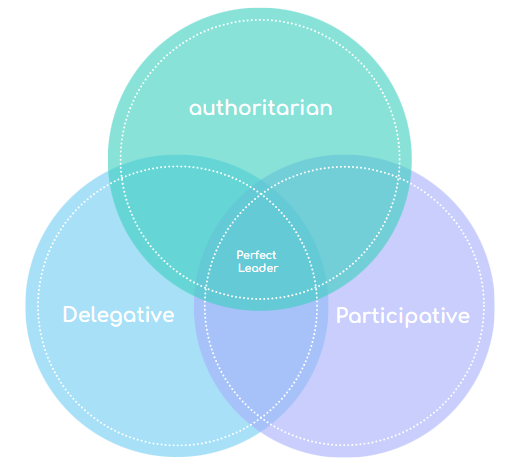
Note. Venn diagram of leadership styles, Gedak, L. 2024
There are many other leadership styles, and when you consider leadership styles, it's important to consider your personality, experience, and goals.
Servant Leadership
Later, in topic three, you will consider your role as an ECE leader in advocating for change and be introduced to ideas for championing the sector, building community and inclusive environments, and celebrating advancements. When examining ECE leadership through this lens, you may find Servant Leadership (Greenleaf, 2002) an impactful approach.
“The servant-leader is servant first… It begins with the natural feeling that one wants to serve first.” - (Greenleaf, 2002, p. 3)
In 1970, Robert Greenleaf first coined Servant Leadership, and this philosophy has stood the test of time and remained an impactful approach, which is no surprise in our tumultuous world. Servant leaders put the well-being and success of those they manage before their own needs. For Servant Leaders, success is measured by the success of their staff and those impacted by their decisions. Read more about Servant Leadership on the Robert K Greenleaf Center for Servant Leadership website.
On the following pages, you will examine the presented leadership styles (Lewin et al., 1939, Greenleaf, 2002) in more detail and consider the leadership style(s) you most closely align with.
References
Aronson, E. (2001). Integrating leadership styles and ethical perspectives. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences/Revue Canadienne des Sciences de l'Administration, 18(4), 244-256.
Greenleaf, R. K. (2002). Servant leadership: A journey into the nature of legitimate power and greatness (25th-anniversary ed.)
Günzel-Jensen, F., Hansen, J. R., Jakobsen, M. L. F., & Wulff, J. (2018). A two-pronged approach? Combined leadership styles and innovative behavior. International Journal of Public Administration, 41(12), 957-970.
Lewin, K., Lippitt, R., & White, R. K. (1939). Patterns of aggressive behaviour in experimentally created “social climates.” The Journal of Social Psychology, 10(2), 269-299.
